day1
手写vector
vector概述
vector是一个动态数组,在内存中连续的块存储元素。
主要维护两个状态信息:capacity和size。
capacity表示分配的内存空间大小(容量),size表示包含的元素数量。当元素数量超过容量,就需要内存重新分配。
动态扩容策略:
指数增长,避免频繁的内存分配操作,减少系统开销。保证插入操作具有常数时间复杂度
随机访问和迭代器
元素连续存储,通过指针运算可实现O(1)时间复杂度的访问
工作原理
内存通常在堆上分配。创建vector对象时,对象本身通常存储在栈上(局部变量),或其他存储区(全局/静态存储区),实际的元素数据在堆上分配。
堆石用于动态内存分配的区域,没有固定的大小限制,所以允许vector在运行时动态增长。
下图中红色表示对象控制结构存储的位置,紫色区域和灰色区域为存储元素的数组的位置, 其中紫色区域表示已经使用, 灰色区域表示未使用
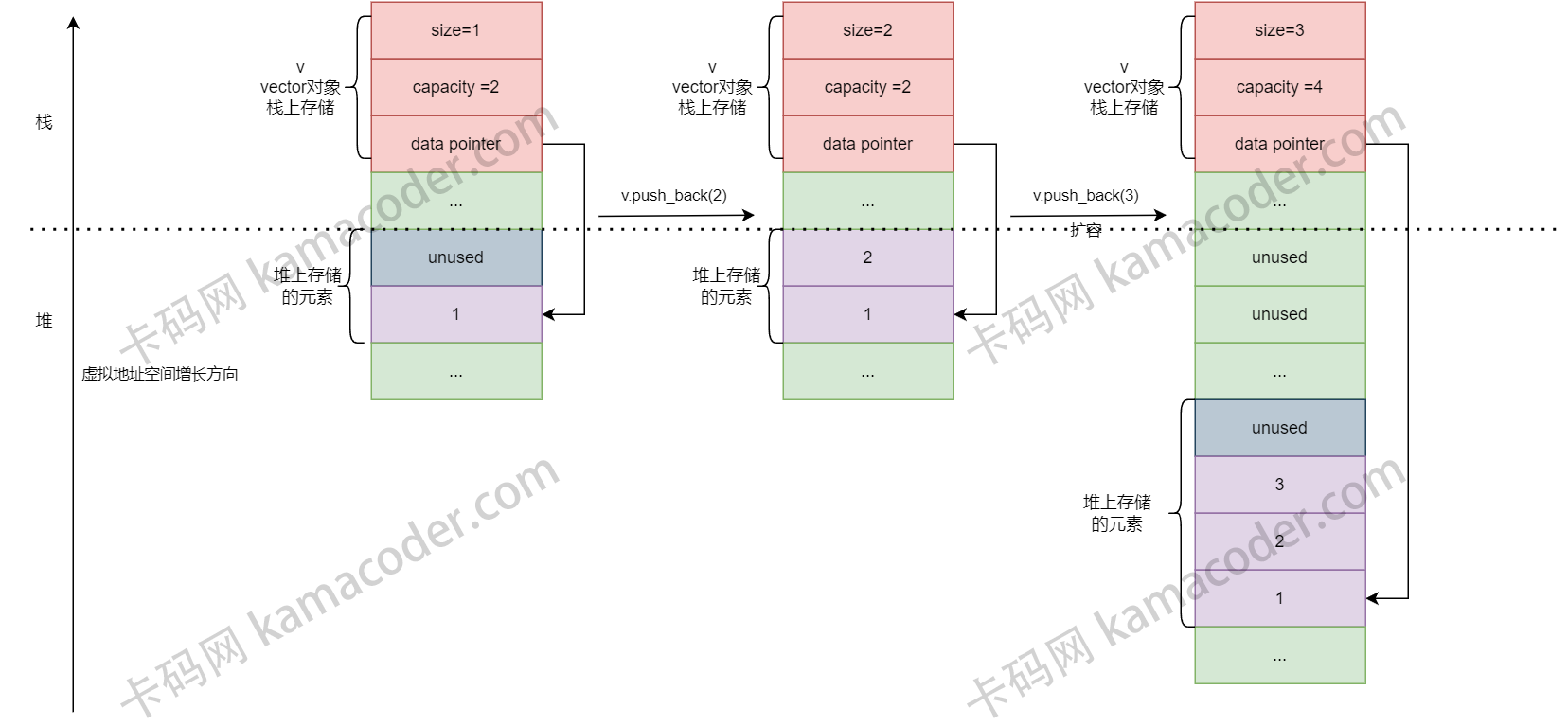
通过分配器std::allocator给数据分配新内存。
vector的实现
vector类包括构造函数、析构函数、拷贝构造函数、拷贝赋值操作符、添加元素、获取元素个数、获取容量、访问元素的功能。
- 构造函数:输出对象,把所有内容(元素,容量,大小)赋值为空或0
- 析构函数:释放指向元素的内存
- 拷贝构造函数:创建一个新的
Vector对象 - 拷贝赋值操作符:允许将一个
Vector对象的值赋给另一个Vector对象 push_back函数:末尾添加一个新元素getSize和getCapacity函数:返回元素数量和容量- 下标操作符:允许下标来访问元素
insert函数:在指定位置插入一个元素pop_back函数:删除末尾元素clear函数:清空元素- 迭代器相关函数
begin和end:begin返回指向第一个元素的指针,end返回指向最后一个元素之后的位置的指针,通常用于表示范围的结束。 printElements函数:打印所有元素。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <stdexcept>
template <typename T>
class Vector
{
private:
T *elements; // 指向动态数组的指针
size_t capacity; // 数组的容量
size_t size; // 数组中元素的个数
public:
// 构造函数
Vector() : elements(nullptr), capacity(0), size(0) {}
// 析构函数
~Vector()
{
delete[] elements;
}
// 拷贝构造函数
Vector(const Vector &other) : capacity(other.capacity), size(other.size)
{
elements = new T[capacity];
std::copy(other.elements, other.elements + size, elements);
}
// 拷贝赋值操作符
Vector &operator=(const Vector &other)
{
if (this != &other)
{
delete[] elements;
capacity = other.capacity;
size = other.size;
elements = new T[capacity];
std::copy(other.elements, other.elements + size, elements);
}
return *this;
}
// 添加元素到数组末尾
void push_back(const T &value)
{
if (size == capacity)
{
// 如果数组已满,扩展容量
reserve(capacity == 0 ? 1 : 2 * capacity);
}
elements[size++] = value;
}
// 获取数组中元素的个数
size_t getSize() const
{
return size;
}
// 获取数组的容量
size_t getCapacity() const
{
return capacity;
}
// 访问数组中的元素
T &operator[](size_t index)
{
// 检查索引是否越界
if (index >= size)
{
throw std::out_of_range("Index out of range");
}
return elements[index];
}
// const版本的访问数组中的元素
const T &operator[](size_t index) const
{
// 检查索引是否越界
if (index >= size)
{
throw std::out_of_range("Index out of range");
}
return elements[index];
}
// 在指定位置插入元素
void insert(size_t index, const T &value)
{
if (index > size)
{
throw std::out_of_range("Index out of range");
}
if (size == capacity)
{
reserve(capacity == 0 ? 1 : capacity * 2);
}
for (size_t i = size; i > index; --i)
{
elements[i] = elements[i - 1];
}
elements[index] = value;
++size;
}
// 删除数组末尾的元素
void pop_back()
{
if (size > 0)
{
--size;
}
}
// 清空数组
void clear()
{
size = 0;
}
// 使用迭代器遍历数组的开始位置
T *begin()
{
return elements;
}
// 使用迭代器遍历数组的结束位置
T *end()
{
return elements + size;
}
// 使用迭代器遍历数组的开始位置(const版本)
const T *begin() const
{
return elements;
}
// 使用迭代器遍历数组的结束位置(const版本)
const T *end() const
{
return elements + size;
}
// 打印数组中的元素
void printElements() const
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
std::cout << elements[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
private:
// 扩展数组容量
void reserve(size_t newCapacity)
{
if (newCapacity > capacity)
{
T *newElements = new T[newCapacity];
std::copy(elements, elements + size, newElements);
delete[] elements;
elements = newElements;
capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
};测试代码
‘’’
int main()
{
// 创建一个 Vector 对象
Vector
int N;
std::cin >> N;
// 读走回车
getchar();
std::string line;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// 读取整行
std::getline(std::cin, line);
std::istringstream iss(line);
std::string command;
iss >> command;
if (command == "push")
{
int value;
iss >> value;
myVector.push_back(value);
}
else if (command == "print")
{
if (myVector.getSize() == 0) {
std::cout << "empty" << std::endl;
continue;
}
myVector.printElements();
}
else if (command == "size")
{
std::cout << myVector.getSize() << std::endl;
}
else if (command == "get")
{
int index;
iss >> index;
std::cout << myVector[index] << std::endl;
}
else if (command == "insert")
{
int index, value;
iss >> index >> value;
myVector.insert(index, value);
}
else if (command == "pop")
{
myVector.pop_back();
}
else if (command == "iterator")
{
if (myVector.getSize() == 0)
{
std::cout << "empty" << std::endl;
continue;
}
for (auto it = myVector.begin(); it != myVector.end(); ++it)
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
else if (command == "foreach")
{
if (myVector.getSize() == 0)
{
std::cout << "empty" << std::endl;
continue;
}
for (const auto &element : myVector)
{
std::cout << element << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
else if (command == "clear")
{
myVector.clear();
}
}
return 0;
}
‘’’



